Graph Tab
 The graph tab converts the split times' numbers to lines, curves, bars, and colours, thereby providing a quick and accessible overview of the information. There are over 30 different graph modes to choose from. The modes are divided into several categories: Time, Place, Performance index, Pack running, Time loss and Legs. The information field under the graph explains the chosen graph's contents and symbols. You can use buttons and text boxes in the tab toolbar to adjust the graph's appearance. For example, you can change zoom level, line thickness, and the axes' limits.
The graph tab converts the split times' numbers to lines, curves, bars, and colours, thereby providing a quick and accessible overview of the information. There are over 30 different graph modes to choose from. The modes are divided into several categories: Time, Place, Performance index, Pack running, Time loss and Legs. The information field under the graph explains the chosen graph's contents and symbols. You can use buttons and text boxes in the tab toolbar to adjust the graph's appearance. For example, you can change zoom level, line thickness, and the axes' limits.
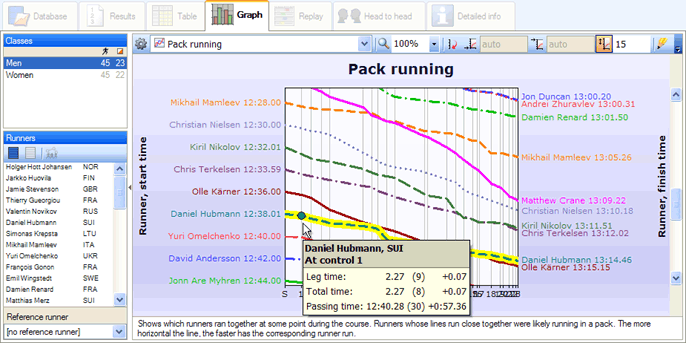
Show information about a graph object
When you hold the mouse cursor over an object in the graph, (for example, a bar or a line segment) a box containing information about the object appears. In some cases, several information boxes are associated with an object. You can press Enter or Space to switch between them.
Show only certain runner and legs
Each graph mode displays a certain number of runners by default. If you want to include more or fewer runners, select the desired runners, either in the runner list on the left in the program window or in thetable tab. In order to include only certain legs, go to the table tab and select the desired legs there. The graph window is updated automatically when selections have been made.
Graph types
WinSplits Pro kan show seven different types of graph.
Print a graph
Choose File > Print or File > Print preview from the menu or click on the buttons  or
or  , respectively, in the header toolbar in order to print a graph on a printer.
, respectively, in the header toolbar in order to print a graph on a printer.
Export a graph
Choose File > Export tab contents from the menu or click on the button  in the header toolbar to export the graph to a picture file in jpg-, gif-, or png-format.
in the header toolbar to export the graph to a picture file in jpg-, gif-, or png-format.
Tab tolbar
The selection of buttons in the tab toolbar depends on the type of graph you are looking at. Therefore, not all of the buttons described below are shown at the same time.
Shortcuts
The following shortcuts can be used for navigating a graph that has vertical and/or horizontal scroll lists.
Tips
- In order to quickly show a graph with just runners from a certain club, right-click on one of that club's runners and choose Select all runners from [club name].